Storage Area Networks have become the backbone of modern data centers. Your business depends on fast data access and zero downtime. A SAN area network layout that is well-planned provides excellent performance and fail-safe protection as well. The proper architecture enables your application to operate without interruptions, and at the same time, it secures the data that is most important. Many organizations struggle with choosing the optimal configuration for their needs.
This article breaks down seven proven SAN area network layout approaches that boost performance and ensure data availability. Each approach offers unique advantages for different workload requirements and budget constraints.
Let’s explore these layouts and find the perfect match for your infrastructure needs.
1. Direct-Attached Topology for Maximum Throughput
Direct-attached layouts connect servers directly to storage arrays without intermediate switches. This approach eliminates network hops and reduces latency significantly. A reliable SAN area network gives this topology the stability and high throughput needed to support demanding workloads with confidence.
Your data travels the shortest possible path from server to disk. Performance metrics show dramatic improvements in read and write operations. Database servers benefit enormously from this streamlined connection method.
Key Benefits of Direct Attachment
The setup costs remain lower than those of complex switched fabrics. You get predictable performance because no other systems share your bandwidth. Troubleshooting becomes easier with fewer components in the signal path.
However, this topology works best for smaller deployments. Scalability challenges emerge as your storage needs grow. You’ll need additional HBAs and cables for each new server connection.
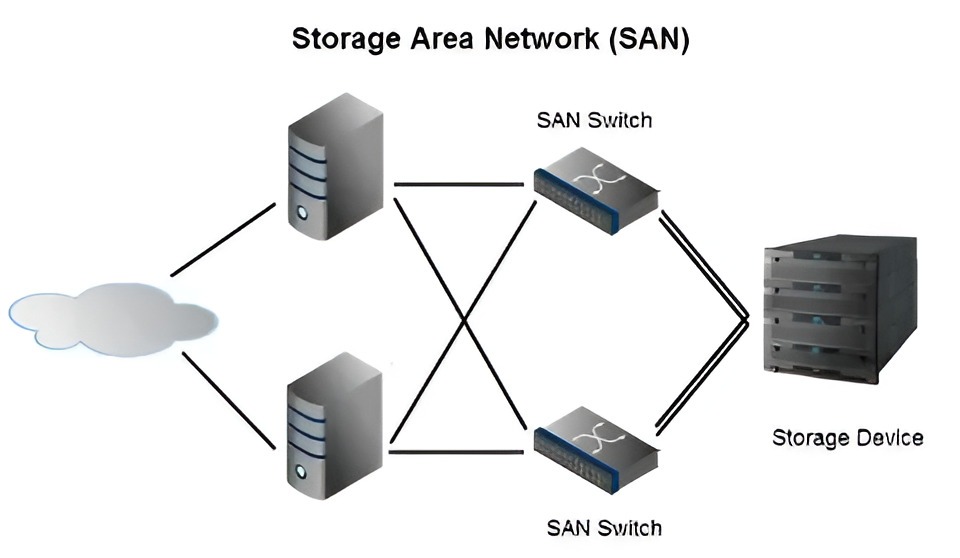
2. Switched Fabric Architecture for Enterprise Scale
Switched fabric layouts use Fibre Channel switches to create flexible SAN networks. Multiple servers access shared storage pools through high-speed interconnects.
For many years, this design pattern has been the king in the world of enterprise data centers. Your infrastructure gets the power to easily extend its capacity by adding more machines instead of upgrading existing ones. Furthermore, storage administrators can allocate resources on the fly across the whole network.
Building Redundant Fabric Layers
Dual-fabric designs protect against single points of failure. Each server connects to two separate switch fabrics simultaneously. Storage arrays maintain connections to both fabrics as well.
A switch failure triggers automatic failover to the secondary path. Your users never notice the transition between fabrics. This redundancy level satisfies strict uptime requirements for mission-critical systems.
3. Mesh Network Design for Ultimate Resilience
Mesh architectures create direct connections between every node in your SAN. This layout offers the highest level of path redundancy available.
Every component can reach any other component through multiple routes. Network congestion becomes nearly impossible under normal operating conditions. Your most demanding workloads get guaranteed bandwidth allocations.
Performance consistency makes this approach ideal for:
- High-frequency trading platforms.
- Real-time analytics engines.
- Medical imaging systems.
- Scientific research clusters.
With more businesses now adopting different SAN layout approaches, the market is continuously rising. As per a report, the global market of Storage Area Network (SAN) is expected to surpass $37.26 billion by 2034.
4. Core-Edge Topology for Cost-Effective Growth
Core-edge layouts balance performance with budget considerations. Powerful core switches handle traffic between storage arrays and edge switches.
Your servers connect to less expensive edge switches near their physical locations. This tiered approach reduces the total switch port count required. Organizations save significantly on infrastructure costs while maintaining good performance.
- The core switches provide high-bandwidth backplanes for inter-array communication.
- Edge switches offer sufficient capacity for server-to-storage traffic.
- You scale by adding edge switches without replacing core infrastructure.
Optimizing Traffic Flow Patterns
Smart zoning policies keep local traffic at the edge layer. Only cross-array operations traverse the core switches. Your network bandwidth gets utilized more efficiently across all segments.
5. Hyperconverged Infrastructure Layouts
Hyperconverged designs integrate compute and storage within the same nodes. Each server contains local storage that joins a distributed pool. Your data gets replicated across multiple nodes automatically. The system maintains copies even when individual servers fail.
This approach appeals to organizations seeking simplified management. You deploy additional nodes to increase both processing power and storage capacity. The architecture scales linearly without separate storage array purchases.
Network requirements shift to high-speed Ethernet connections. Software handles all the complexity of data placement and protection. Your IT team manages everything through unified interfaces.
6. Active-Active Array Configuration
Active-active layouts use multiple storage controllers simultaneously. Both controllers process I/O requests concurrently instead of waiting in standby mode.
Your storage investment delivers double the performance potential. Load balancing algorithms distribute operations across available controllers. The system automatically redirects traffic when one controller experiences issues.
This configuration works exceptionally well for:
- Virtualized server environments
- Email and collaboration platforms
- Web application backends
- Development and testing systems
Modern arrays support this mode natively. You simply enable the feature through management software. Performance gains appear immediately without architectural changes to your SAN fabric.
7. Tiered Storage Architecture
Tiered layouts match data placement with performance requirements. Your most active datasets reside on the fastest storage media available.
- Flash arrays handle hot data that needs instant access.
- Traditional spinning disks store warm data with moderate activity levels.
- Archive systems hold cold data accessed infrequently.
Automated policies move data between tiers based on usage patterns. The system tracks access frequencies and adjusts placement accordingly. Your storage budget stretches further by avoiding overprovisioning premium media.
The SAN fabric delivers adequate throughput for each tier’s characteristics. Users get fast response times for their active working sets while historical data remains accessible.
Conclusion
These seven SAN area network layout approaches each solve specific challenges in modern data centers. Your choice depends on performance needs and redundancy requirements, and available budget. Select the layout that aligns with your business objectives and technical constraints. Remember that hybrid approaches combining multiple strategies often yield the best results. Your storage architecture should evolve alongside your organization’s changing requirements.